- Lifetime Solutions
VPS SSD:
Lifetime Hosting:
- VPS Locations
- Managed Services
- Support
- WP Plugins
- Concept

The global blockchain market reached $31.28 billion USD in 2024 and continues accelerating toward an estimated $246 billion by 2030. Behind this explosive growth stands a critical shortage of skilled professionals: blockchain developers. These specialized software engineers command average salaries of $146,250 to $150,000 annually in the United States, with experienced developers earning up to $187,500. Whether you’re contemplating a career shift or launching into tech for the first time, understanding what blockchain developers do and how to become one is essential.
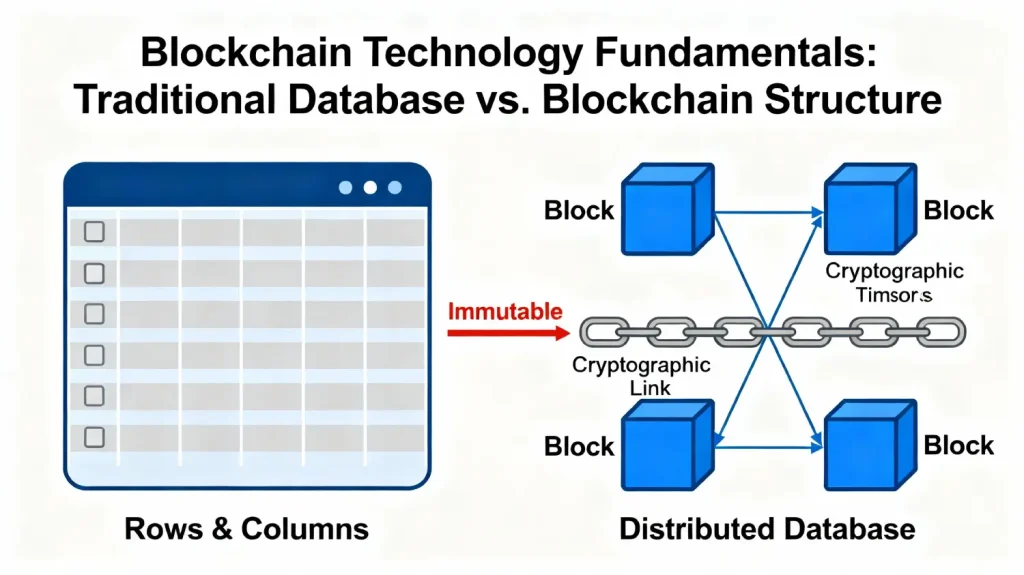
Before diving into blockchain development, grasp the core technology foundation.
A blockchain is a distributed database that stores information and arranges it in a different way compared to traditional databases. Whereas traditional databases organize data in rows and columns to create a table, blockchains store data in groups referred to as blocks. Each block has a specific storage capacity, and once it is full, it closes and cryptographically joins the foregoing block.
This linking creates an immutable chain of blocks, hence the name “blockchain.” The cryptographic timestamp generated during each link provides permanent, unchangeable records that verify the accuracy of transactions and sensitive information. This fundamentally differs from traditional databases, which are typically controlled by a central authority managing and maintaining sensitive data.
Decentralization: No single authority controls the network. Instead, thousands of independent nodes (computers) maintain identical copies of the blockchain, eliminating single points of failure.
Transparency: All authorized participants can view the same verified data, eliminating disputes and improving accountability.
Immutability: Once data is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted without invalidating the entire chain—a feature that makes blockchains extraordinarily secure.
Security: Cryptographic algorithms protect sensitive information, with private and public keys ensuring only intended recipients can access specific data.
A blockchain developer is a software developer who specializes in developing, supporting, and designing blockchain applications and systems. They use the peculiarities of blockchain technology to address real-life issues and invent new possibilities.
1. Core Blockchain Developers
Core blockchain developers work on the foundational layer of blockchain systems. They design protocols, develop security patterns, and supervise the network as a whole. This role involves:
Core developers normally work for blockchain platforms like Ethereum, Solana, or Hyperledger, directly contributing to the development.
2. Blockchain Software Developers
Blockchain software developers build applications that run on top of existing blockchain platforms. Rather than creating the blockchain itself, they use established protocols to create decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts. Their responsibilities include:
This path is typically more accessible for developers transitioning into blockchain, as it requires understanding existing platforms rather than building from scratch.

The smart contract is one of the most powerful blockchain-based innovations that developers develop. A smart contract is a computer program or self-executable code that is directly stored on a blockchain and can be used to enforce agreements between two parties under pre-existing conditions.
Unlike traditional contracts requiring third-party intermediaries (lawyers, escrow services, banks), smart contracts execute automatically and instantaneously. The classic analogy is a parking meter: you insert the correct payment, and the meter automatically validates your parking time without requiring any human intervention or authorization.
Financial Services: Automated loan disbursement, insurance claims processing, and derivatives settlement.
Supply Chain: Automatic payment release when products reach specific locations, verified through sensors integrated with the blockchain.
Real Estate: Property transfers execute automatically upon payment receipt, eliminating escrow delays.
Healthcare: Medical records transfer automatically between providers with patient authorization stored on the blockchain.
Governance: Voting mechanisms that execute decisions automatically based on smart contract conditions.
Smart contracts eliminate inefficiency, reduce costs, and ensure transparent, tamper-proof execution of complex business logic.
To be a successful blockchain developer, one is expected to have knowledge in various areas. The technical environment is more specialized and has a wider geography compared to normal software development.
Solidity: Ethereum smart contracts are primarily developed in this language. Solidity syntax is similar to JavaScript with additions of blockchain considerations and syntax.
Rust: Increasingly vital for developing smart contracts on platforms like Solana and Arbitrum Stylus. Rust offers superior performance and memory safety, making it ideal for high-speed blockchain systems.
JavaScript/TypeScript: Important to create front-end interfaces to communicate with blockchains. Ethers.js and Web3.js libraries allow JavaScript developers to develop apps that are connected to blockchains.
Python: Popular for blockchain analysis, testing frameworks, and rapid prototyping due to its versatility and readability.
Go and C++ : Used in core blockchain development and infrastructure projects.
Cryptography is an integral, non-negotiable component of blockchain development. Developers must understand:
Distributed systems are also essential to blockchain developers, as blockchains are distributed networks. Essential knowledge includes:
The knowledge of various blockchain structures can be used to guide the developer to select the right platform to use in certain applications.
| Blockchain Type | Characteristics | Use Cases | Examples |
| Public | Permissionless, fully decentralized, anyone can join | Cryptocurrencies, DeFi, public records | Bitcoin, Ethereum |
| Private | Permissioned, single entity control, restricted access | Enterprise systems, private finance | Hyperledger Fabric, Corda |
| Consortium | Multiple organizations share control | Industry collaborations, supply chains | Global Shipping Business Network |
| Hybrid | A combination of private and public elements | Enterprise with public verification needs | Ripple, Dragonchain |
Data structures: Understanding Merkle trees, bloom filters, and other specialized data structures used in blockchain systems. The University of California, San Diego’s Data Structures Specialization provides comprehensive coverage.
Web development: Frontend skills using React, Vue.js, or Angular for building user interfaces for dApps and blockchain applications.
Testing and debugging: Creating comprehensive test suites for smart contracts and blockchain applications, as bugs can result in millions of losses.
Version control: Git proficiency for collaborative development and code management.
Provided you do not have experience in programming, begin with computer science fundamentals. Online platforms provide faster tracks that are directed towards those who want to become blockchain developers. The Junior Software Developer Professional Certificate at Amazon offers an effective entry level in months, and not years, as it introduces the fundamentals of programming.
It is better to master a single language first and then go further. The most successful transitions begin with Python or JavaScript since they are readable and have existing blockchain libraries.
Once comfortable with programming, dive into blockchain technology itself. Start with entry-level courses like “Introduction to Blockchain Technologies” on Coursera or Udacity, which teach you how blockchains work without requiring deep technical expertise.
Key concepts to master at this stage:
This is where abstract blockchain knowledge becomes practical development. Ethereum offers the most mature ecosystem for smart contract learning, with extensive resources and community support.
Getting Started with Solidity:
Professional blockchain development requires proficiency with specialized tools:
Truffle Suite – Allows the creation, test, and execution of smart contracts by including built-in testing structures and contract assembly.
Hardhat – Modern alternative to Truffle offering more flexibility and better developer experience for Ethereum development.
Ganache – Creates a personal blockchain for rapid testing without deploying to test networks.
Ethers.js/Web3.js – JavaScript libraries enabling applications to interact with Ethereum and other blockchains.
MetaMask – Browser extension managing digital wallets and enabling dApp interactions.
Theory alone doesn’t create developers. Practical experience is essential:
Build Simple Projects:
Contribute to Open Source:
Participate in Hackathons:
Deploy to Testnets:
Blockchain technology evolves rapidly. Successful developers maintain continuous learning:
Follow Industry News:
Explore Specializations:
A degree in computer science provides competitive advantages and foundational knowledge:
However, blockchain is too new for most universities to teach comprehensively. You’ll typically combine a CS degree with specialized blockchain bootcamps or online courses.
Many successful blockchain developers built careers through self-directed learning:
The key to self-learning success is discipline, consistent effort, and building a substantial portfolio of projects demonstrating your capabilities.
Many successful blockchain developers combine strategies:
This approach balances speed with depth while building an impressive portfolio.
The blockchain developer job market shows exceptional growth and compensation:
Average Compensation (2026):
Job Growth Projections:
Factors Influencing Salary:
Blockchain Companies – Native blockchain platforms and protocol developers (Ethereum Foundation, Solana Labs, Cosmos)
Cryptocurrency Exchanges – Coinbase, Kraken, and Binance employ developers for trading platforms and security
DeFi Protocols – Uniswap, Aave, Curve hire developers for decentralized finance systems
Traditional Finance – JPMorgan, Goldman Sachs, institutional investors entering blockchain
Enterprise Blockchain – Companies implementing private blockchains for supply chains, identity, or records
Web3 Startups – Thousands of startups building dApps, wallets, and blockchain infrastructure
The blockchain industry offers exceptional remote work opportunities:
While cryptocurrencies capture media attention, enterprise blockchain applications represent the largest growth opportunity:
Walmart adopted blockchain in food traceability, which decreased the food tracking from 7 days to 2.2 seconds. All movements of ingredients, such as farm to the store, are permanently documented and can be checked immediately. In the case of contamination, the whole batch of contaminated food can be identified and recalled within a few seconds to avoid health hazards on a large scale.
Developers building supply chain solutions need expertise in IoT integration, real-time data validation, and complex multi-party smart contracts.
JPMorgan JPM Coin and Ripple XRP settle international transactions in seconds instead of days, eliminating intermediary banks and reducing costs by 30-50%. As currencies digitize and central banks adopt blockchain infrastructure, demand for payment rail developers grows exponentially.
Identity systems that use blockchain technology eliminate frequent KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) verification. Users manage their identity credentials and only provide the necessary details to every party. Very early involves the Verify Credentials platform and the government digital ID programs (the Republic of Georgia uses blockchain to issue land titles) by IBM.
Sahara with blockchain helps patients to have secure and mobile medical records. Verified records are instantaneously accessed by the providers in cases of emergency and do not need to be documented physically. The Learning Machine is issuing diplomas put in blockchain, which makes the documents tamper-resistant.
Power Ledger enables peer-to-peer energy trading on blockchain networks, allowing solar panel owners to sell excess electricity directly to neighbors, bypassing utility companies.
Ethereum Ecosystem:
Alternative Platforms:
Development Libraries:
Reality: Identity systems that use blockchain technology eliminate frequent KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) verification. Users manage their identity credentials and only provide the necessary details to every party. Very early involves the Verify Credentials platform and the government digital ID programs (the Republic of Georgia uses blockchain to issue land titles) by IBM.
Reality: Blockchain applications extend far beyond crypto. Supply chains, healthcare, identity, voting, education, real estate, and energy represent massive opportunities. Enterprise blockchain represents the largest market segment.
Reality: Although it is necessary to know the principles of cryptography, you do not have to develop new cryptography. Libraries of cryptography are complex and are present. It is not the generation of cryptography that you are going to perform, but rather its implementation and application.
Reality: Security is paramount; mistakes can result in million-dollar losses or compromise user funds. The field demands continuous learning, rigorous testing, and deep focus on security details. It’s challenging, rewarding work, not a shortcut to wealth.
Reality: The current development of blockchain uses JavaScript/TypeScript on the frontend, Solidity or Rust as smart contracts, and possibly Python on the backend. The knowledge of more than one language is becoming the norm.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZK) – Privacy-preserving cryptographic techniques enabling transactions without revealing details. Demand for ZK specialists is rapidly increasing.
Cross-Chain Interoperability – Protocols enabling seamless interaction between different blockchains. Bridges and interoperability solutions represent a growing specialization.
Layer 2 Scaling – Technologies like Optimism and Arbitrum enable thousands of transactions per second on Ethereum. Layer 2 expertise is increasingly in demand.
Quantum-Resistant Cryptography – As quantum computing advances, traditional cryptography becomes vulnerable. Developing quantum-resistant blockchain systems is an emerging frontier.
Sustainability and Energy-Efficient Consensus – Moving beyond Proof of Work toward environmentally friendly mechanisms. Specialization in green blockchain technology is growing.
Becoming a blockchain developer offers exceptional opportunities in an industry reshaping digital infrastructure. Whether you’re drawn to cryptocurrency, enterprise blockchain applications, or the broader Web3 movement, the field welcomes dedicated learners willing to invest the effort.
The blockchain industry needs skilled developers. The challenge, compensation, and impact make blockchain development one of the most rewarding technology careers available. Your blockchain development journey can begin today.

Hassan Tahir wrote this article, drawing on his experience to clarify WordPress concepts and enhance developer understanding. Through his work, he aims to help both beginners and professionals refine their skills and tackle WordPress projects with greater confidence.