- Lifetime Solutions
VPS SSD:
Lifetime Hosting:
- VPS Locations
- Managed Services
- Support
- WP Plugins
- Concept
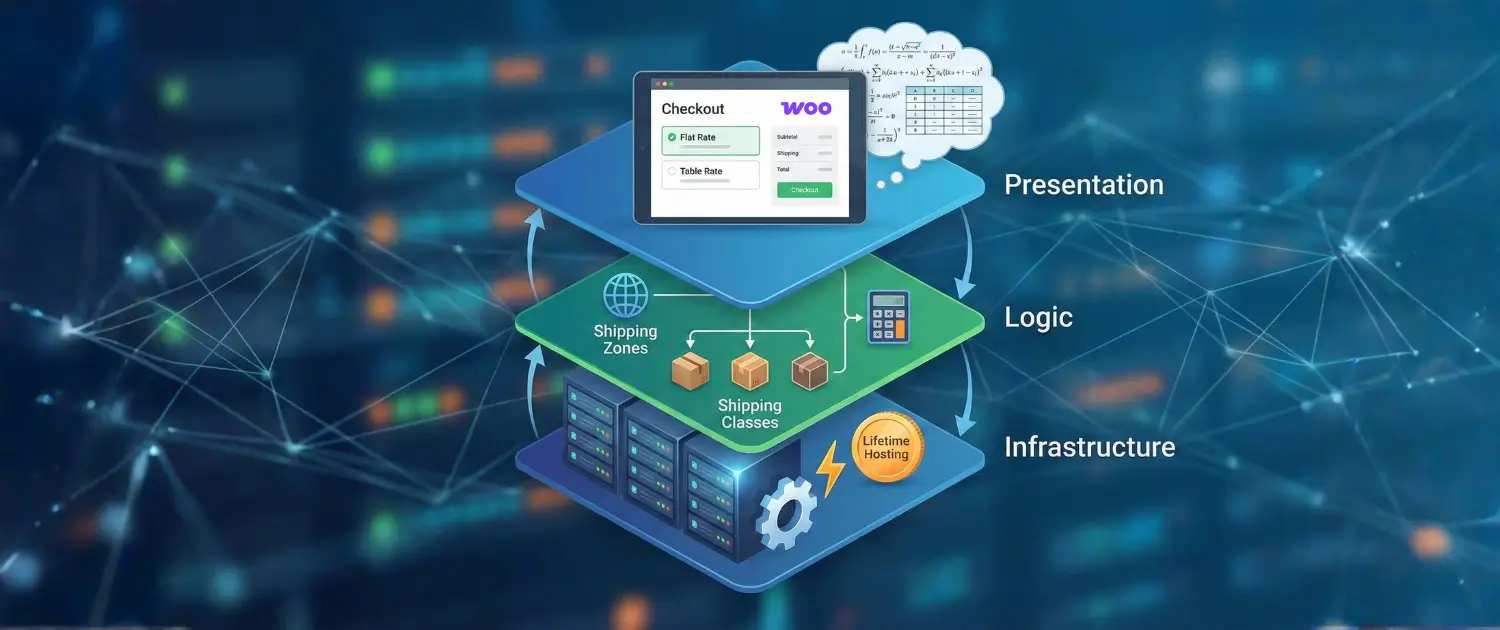
In the fast-moving world of digital business, shipping is the bridge between your online store and your customer’s front door. For a business owner or store manager, understanding how your shipping is set up is more than just a technical task, it is a strategy that directly affects your sales and your profits.
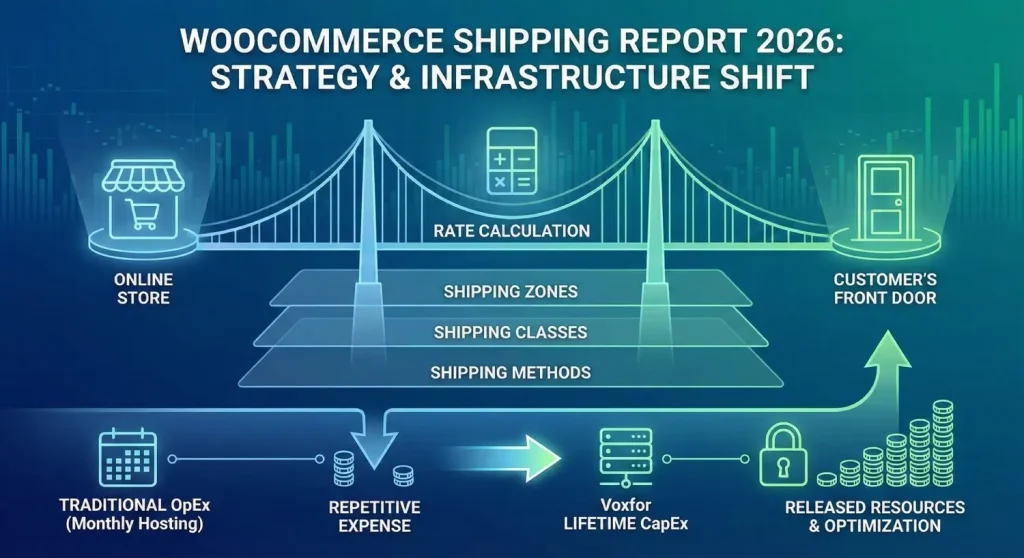
This is a full report that exhaustively covers the WooCommerce shipping ecosystem in the year 2026. It breaks down the technical stratifications of Shipping Zones, Classes, and Methods, examines the mathematical reasoning of the rate calculation and the evaluation of the seriousness of server infrastructure in providing real-time shipping information. Moreover, this report questions the traditional OpEx models of operation of hosting based on Voxfor through the analysis of the new lifetime infrastructure solutions offered by Voxfor. Moving away from repetitive monthly expenses to capital expenditure models, businesses will be able to change the economics of their units fundamentally and release resources to optimize their logistical processes.
Shipping in the current e-commerce world is no longer an after-sale consideration, but a major factor in making the purchase decision in the first place. The global marketplaces that provide almost instant satisfaction have radically transformed consumer demands, and the independent retailers are compelled to adopt advanced logistical methodologies to stay competitive. The algorithm along which a WooCommerce store will compute, present, and implement shipping options is, hence, no less essential than a product catalog.
Shipping experience starts as soon as the user puts something in their cart. In the background, there is a complicated negotiation involving the browser of the user, the server hosting it, the database and possibly third-party carrier APIs. This bargaining needs to be decided within milliseconds, or it will be frictional. There is a direct correlation between cart abandonment and a delay in shipping rates, which is usually due to poor server performance or inefficient database queries. Therefore, the technical structure of shipping arrangements is irrevocably bound to the generation of revenue.
Once a customer comes to the checkout page, they have to make a heavy dynamic operation to the server. The checkout page is also session-specific, unlike product pages that can be cached as static HTML. It will need to compute tax depending on the address in question, a real-time check of inventory and look up of shipping regulations against the weight and size of the cart contents.
When the hosting facilities are constructed upon legacy architecture (e.g., standard HDD storage or Apache servers without object caching), then this calculation process provides a bottleneck. The spinning wheel, when shipping rates are being updated, is a conversion murderer. This fact is why there should be a migration to high-performance hosting offerings that use NVMe storage and advanced caching systems such as Redis and LSCache, which are technologies at the heart of the next-generation offering of providers such as Voxfor.
Another distinct aspect of the 2026 hosting Landscape is the duplication of cost models. Conventional managed hosting is based on a SaaS (Software as a Service), which takes out monthly fees that increase with success. New models, on the other hand, such as Voxfor “Lifetime Hosting” have an alternative to Capital Expenditure (CapEx). A business can pay a single up-front charge for a lifetime enterprise-level hosting and avoid a fixed cost altogether.
Such a financial restructuring applies to shipping strategy since shipping tends to be used as a loss leader. When the amount of money that a store owner can save in hosting costs can be as high as $500-1000/year, the capital could be re-invested to underwrite shipping rates, which is Free Shipping to the customer, that would not reduce net margins. This interaction between infrastructure economics and logistical pricing strategy is one of the major themes of this report.
Before diving into the configuration of WooCommerce, one must secure the foundation. Shipping calculations are database-intensive. A complex store might have 50 shipping zones, each with 10 different rates based on weight classes. A single checkout request triggers a cascade of SQL queries to find the matching zone and calculate the cost.
Voxfor has positioned itself as a specialist in high-performance WooCommerce environments. Their architecture addresses the specific bottlenecks of shipping calculations through three primary technologies: LiteSpeed Enterprise, NVMe Storage, and Redis Object Caching.
| Feature | Standard Hosting Impact | Voxfor Optimization | Impact on Shipping |
| Web Server | Apache/Nginx processes requests linearly. | LiteSpeed Enterprise uses event-driven architecture. | Handles concurrent checkout requests during flash sales without hanging. |
| Storage | SATA SSDs limit Input/Output operations (IOPS). | NVMe SSDs offer 6x faster data transfer rates. | Drastically reduces the time to query the database for shipping zones and rates. |
| Caching | Standard page caching breaks checkout. | LSCache + ESI (Edge Side Includes). | Allows the “static” parts of a checkout page to be cached while keeping shipping data dynamic. |
| Object Cache | Database queried for every page load. | Redis Object Cache stores query results in RAM. | Instant retrieval of shipping zones for repeat visitors or similar addresses. |
For a WooCommerce store, longevity is the goal. Voxfor Lifetime Hosting Solutions offers a strategic advantage.
Shipping data contains Personally Identifiable Information (PII), addresses, phone numbers, and names. Security is non-negotiable. Voxfor integrates Imunify360 and a Web Application Firewall (WAF) directly into the server stack. This protects against SQL injection attacks that might attempt to exploit shipping calculation forms or intercept customer data during the checkout process.
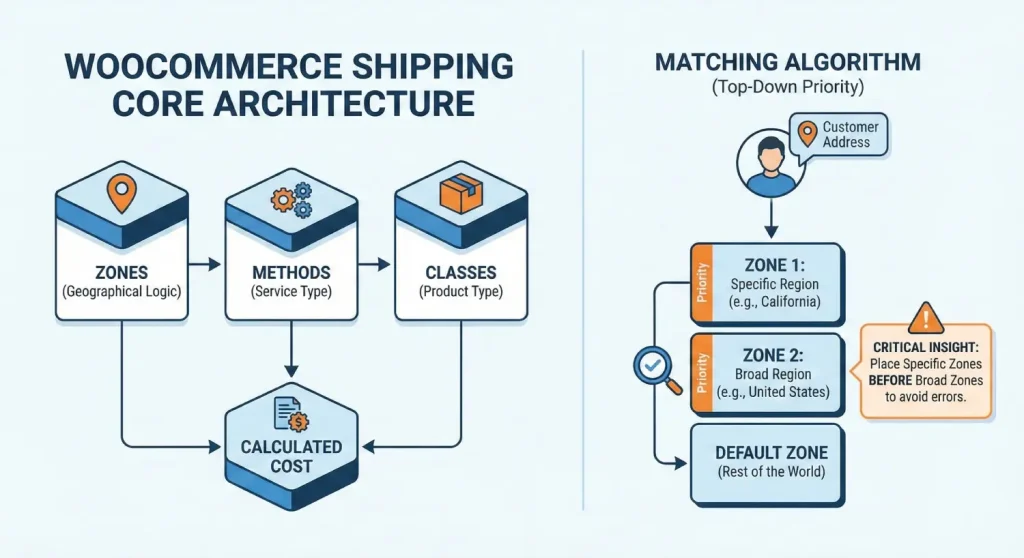
To learn WooCommerce shipping, one must understand the three pillars of its architecture: Zones, Methods, and Classes. These three elements interact hierarchically to determine the final cost presented to the customer.
A Shipping Zone is a defined geographical region to which a specific set of shipping methods and rates applies. It is the “If” condition in the shipping logic: If the customer is in Zone A, then offer Method X and Y.
WooCommerce matches a customer to a zone using a top-down priority system.
Critical Configuration Insight: This hierarchy is the most common source of configuration errors. A broad zone (e.g., “United States”) placed above a specific zone (e.g., “California”) will result in California customers being matched to the generic US zone, potentially denying them specific local shipping rates. The rule of thumb is: Specific beats General. Place the smallest geographical regions at the top of the list.
Three levels of granularity can define zones:
Technical Note on Wildcards: When using wildcards in the Voxfor optimized environment, the database query uses LIKE operators. For example, 902* matches 90210 and 90288-1234. This is computationally efficient and recommended over listing thousands of individual zip codes, which can bloat the wp_woocommerce_shipping_zone_locations table and slow down the checkout query.
Once a zone is matched, the Shipping Methods assigned to that zone are displayed to the user. Core WooCommerce includes three standard methods:
Shipping Classes allow for product-specific shipping rules. They group items with similar logistical characteristics, such as “Heavy,” “Fragile,” or “Bulky”.
The “Flat Rate” method is very simple. While it appears to offer just a fixed price, it contains a powerful algebraic engine capable of handling complex pricing models without external plugins.
To configure a flat rate:
The core fields are Title, Tax Status, and Cost.
The “Cost” field accepts not just numbers, but mathematical formulas and shortcodes. This allows for dynamic pricing based on cart contents.
The [qty] placeholder represents the total number of items in the cart.
The [fee] placeholder allows charges based on the total value of the cart.
When Shipping Classes are defined, the Flat Rate settings screen expands to show additional fields for each class.
Expert Recommendation: For most B2C retailers, the Per Order setting is superior. Customers typically view shipping as a single service for the entire package. Charging them separate fees for different items in the same box (Per Class) is often perceived as “hidden fees” and drives cart abandonment.
Shipping Classes are the mechanism by which WooCommerce handles inventory diversity. If a store sells both grand pianos and sheet music, a single flat rate is impossible. Classes bridge this gap.
Classes should be defined based on logistical attributes, not product categories.
To create classes:
This is a manual but necessary step for accurate calculations.
A common oversight is failing to define a cost for the “No Shipping Class” field in the Flat Rate settings.
Free Shipping is arguably the most powerful marketing tool in e-commerce, but technically it is a “Shipping Method” that requires careful configuration to avoid margin erosion.
To enable Free Shipping:
| Requirement | Behavior | Use Case |
| N/A | Always free. | Use for a “Local Delivery” zone or special promotions. |
| Valid Coupon | Requires a code (e.g., “FREESHIP”). | targeted marketing campaigns. |
| Minimum Order Amount | Cart total > $X. | Increasing Average Order Value (AOV). |
| Min Amount OR Coupon | Either condition triggers it. | Flexible loyalty programs. |
| Min Amount AND Coupon | Both required. | Protecting margins on low-value orders. |
A frequent source of customer frustration involves the interaction between discount coupons and free shipping thresholds.
When Free Shipping is available, WooCommerce still displays the other methods (e.g., Flat Rate) by default. This confuses customers: Why would I pay $5 if Free Shipping is an option?
For businesses with physical retail footprints or warehouses, Local Pickup is a bridge between the digital and physical worlds (O2O).
The most common configuration error with Local Pickup involves putting it in the wrong zone.
Tax laws for pickup often differ from those for delivery.
Retailers often incur costs to pick and pack orders for collection. The Local Pickup method allows for a Cost field.
As a business scales, simple Flat Rates often fail to capture the nuance of carrier costs. Shipping a feather is cheap; shipping a barbell is expensive. Flat rates treat them equally. This necessitates Table Rate Shipping.
Table Rate Shipping transforms the shipping calculation from a linear equation into a multi-dimensional matrix. It allows for rules based on:
WooCommerce Core does not support Table Rates. This requires premium plugins like WooCommerce Table Rate Shipping or Flexible Shipping.
Table Rate lookups are computationally heavier than Flat Rates. A complex store might have a table with thousands of rows (e.g., different rates for every zip code/weight combination).
Global shipping introduces exponential complexity: variable carrier rates, customs documents, and duties.
For international shipments, “Flat Rates” are risky. A $50 flat rate to “Europe” might cover a shipment to Paris ($30), but lose money on a shipment to rural Norway ($70).
To get an accurate rate, the carrier needs to know not just the weight of the products, but how they fit into a box.
Real-time rates introduce an external dependency. If the FedEx API takes 3 seconds to respond, your checkout hangs for 3 seconds.
Even with a perfect setup, issues arise. This section details how to diagnose and fix common shipping anomalies using the tools available in WooCommerce and the Voxfor panel.
This is the single most common error message in WooCommerce. It means the logic chain broke.
WooCommerce uses a script called wc-ajax=get_refreshed_fragments to update the mini-cart (the icon in the header) without reloading the page.
To show “Estimated Shipping” on the product page, the site needs to guess the user location (GeoIP).
As we look toward the latter half of the 2020s, shipping is moving toward autonomy.
The manual process of copying addresses to a label printer is obsolete.
Artificial Intelligence is beginning to play a role in:
Running these AI models (even light inference) requires significant computational power. Voxfor commitment to high-performance hardware (NVMe/LiteSpeed) positions it as a “Future-Ready” host capable of supporting the next generation of AI-driven commerce plugins.
Shipping is not a setting; it is a system. It relies on the seamless integration of geographical data, product attributes, mathematical logic, and server performance.
By learning these three layers, Infrastructure, Logic, and Presentation, store owners can transform shipping from a logistical burden into a competitive asset.

Hassan Tahir wrote this article, drawing on his experience to clarify WordPress concepts and enhance developer understanding. Through his work, he aims to help both beginners and professionals refine their skills and tackle WordPress projects with greater confidence.