- Lifetime Solutions
VPS SSD:
Lifetime Hosting:
- VPS Locations
- Managed Services
- Support
- WP Plugins
- Concept
Hugging Face has transformed the interface of developers and data scientists with artificial intelligence and machine learning models. Being the most popular open-source AI platform, Hugging Face democratizes access to the state-of-the-art transformer models. It offers a collaborative ecosystem in which millions of users can find, create and launch AI applications. Another unique feature of the platform is Hugging Face Spaces, which allows developers to convert pre-trained models into interactive and shareable web apps without having to operate intricate infrastructure.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the technical capabilities of both Hugging Face and Spaces, examining how you can leverage these tools to build, deploy, and monetize AI applications efficiently.
Hugging Face is an open-source platform and community dedicated to making artificial intelligence accessible to everyone. Founded on the principle of democratizing AI, it serves as a central hub for machine learning models, datasets, and applications.
Hugging Facebook Model Hub represents a distributed storage with more than 100,000 ready-made models. This huge body of work cuts across various fields, such as natural language processing, computer vision, audio processing, and multimodal AI. Rather than having to train models directly, as a process consuming large amounts of computational resources and expertise, developers can download and retrain existing state-of-the-art models for the specific scenarios of their application.
Popular models available on the Hub include BERT, GPT series, LLaMA, DistilBERT, RoBERTa, and many domain-specific models. This eliminates the need for expensive computational infrastructure and accelerates time-to-market for AI applications.
The Transformers library is a powerful Python library providing easy access to thousands of pre-trained models through a unified API. Built on top of PyTorch and TensorFlow, it abstracts away the complexity of model architecture, tokenization, and inference.
The library’s core components include:
With the Pipeline API, complex AI functions can be achieved in a few lines of code. Sentiment analysis can be achieved with the following:
from transformers import pipeline
classifier = pipeline("sentiment-analysis")
result = classifier("I love using Hugging Face!")
print(result)Beyond the Model Hub, the Hugging Face Hub acts as a collaborative platform where developers can host, manage, and share their models. Users can create organizations, manage team permissions, and control model visibility (public or private). This infrastructure eliminates the need to set up your own model serving infrastructure.
Spaces: Interactive Application Hosting
Hugging Face Spaces allows developers to host interactive demonstrations and full-stack applications directly on the platform. This is where Spaces truly shines as a unique offering.
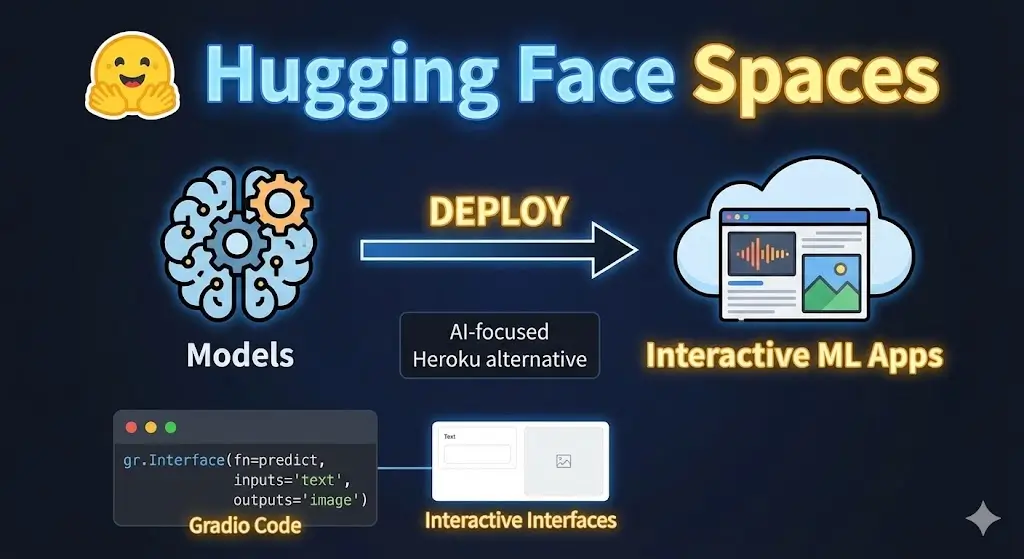
Hugging Face Spaces is a free hosting service that allows developers to create, deploy, and share interactive machine learning applications. Built on top of the Model Hub, Spaces enables you to turn your models into fully functional web applications that other users can interact with in real-time.
Think of Spaces as a simplified, AI-focused Heroku alternative specifically designed for machine learning applications. You can upload your application code, connect it to Hugging Face models, and have it running publicly within minutes—all without managing servers, containers, or deployment pipelines.
Gradio is a Python library that enables you to build interactive web interfaces for machine learning models with minimal code. It’s perfect for creating quick demos and proof-of-concept applications.
Gradio handles the UI/UX complexity, allowing you to focus on model logic. You define inputs (text, images, audio), outputs, and a processing function, and Gradio automatically generates a professional-looking web interface.
Example Gradio application:
import gradio as gr
from transformers import pipeline
# Load a text generation model
generator = pipeline("text-generation", model="gpt2")
def generate_text(prompt):
result = generator(prompt, max_length=50, num_return_sequences=1)
return result['generated_text']
# Create interface
demo = gr.Interface(
fn=generate_text,
inputs=gr.Textbox(label="Enter your prompt"),
outputs=gr.Textbox(label="Generated text"),
title="Text Generator",
description="Generate text using GPT-2"
)
demo.launch()Streamlit is another popular framework for building data applications and machine learning interfaces. It’s more powerful than Gradio for complex, multi-page applications, but requires slightly more code.
Streamlit is ideal for building:
Example Streamlit application:
import streamlit as st
from transformers import pipeline
st.title("Sentiment Analysis App")
classifier = pipeline("sentiment-analysis")
user_text = st.text_area("Enter text to analyze:")
if st.button("Analyze"):
result = classifier(user_text)
st.write(result)Docker Support
Hugging Face Spaces supports arbitrary Docker containers if you want to use them in an advanced use case, which may need custom environments. This puts full control over dependencies, system packages and runtime configuration.
Static Spaces:
You can also create static Spaces using plain HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, perfect for simple dashboards or documentation.
Free Hosting with Resource Options
Spaces offers a free hosting service along with the standard specified resources: 16GB RAM and 8 CPU cores. In the case of applications that need to be accelerated using the GPU, you can upgrade to paid packages that include NVIDIA A100 or T4 GPUs.
Git-Based Deployment
Spaces uses Git for version control and deployment. You clone the Space repository, make changes locally, and push updates, similar to deploying to GitHub Pages. This git-native workflow is intuitive for developers.
Persistent Storage
Spaces can store persistent data using file systems, enabling applications that accumulate results or user data over time.
Environment Variables and Secrets
Spaces also offers secret management in the form of environment variables, so you do not have to use hardcoded API keys, tokens, and other sensitive credentials in your application code.
Automatic Restart and Error Handling
If your application crashes, Spaces automatically restarts it. Error logs are accessible through the platform’s debugging interface.
No Setup Required
Compared to conventional deployments, where one needs to know Docker, nginx setup, or Kubernetes orchestration, space hides infrastructure management.
Hugging Face is particularly powerful for NLP tasks. The Transformers library provides models optimized for:
Text Classification
Perform sentiment analysis, spam detection, topic categorization, and intent classification. Pre-trained models like DistilBERT can classify text in milliseconds.
Named Entity Recognition (NER)
Extract entities like names, locations, organizations, and dates from text. Models like RoBERTa-base-ner are specifically fine-tuned for this task.
Question Answering
Extractive QA model: Use extractive QA models to find answers in documents. Such models as DistilBERT or ELECTRA have high accuracy in identifying answer spans.
Text Summarization
Summarize long documents automatically using sequence-to-sequence models like BART or T5.
Machine Translation
Translate text between languages using pre-trained translation models.
Text Generation
Create human textual data with the help of a text model, such as GPT-2, Llama, or Mistral, and make chatbots, content generation, and creative applications possible.
Beyond NLP, Hugging Face hosts advanced vision models:
Image Classification
Classify images into predefined categories using models like ViT (Vision Transformer) or ConvNeXt.
Object Detection
Find and locate objects in images with DETR (Detection Transformer) or YOLO networks and allow security systems, inventory systems and autonomous driving applications.
Image Segmentation
Perform semantic or instance segmentation using models like Segformer for autonomous driving, medical imaging, or satellite imagery analysis.
Zero-Shot Image Classification
Use CLIP (Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training) to classify images without training on specific labels—incredibly powerful for open-ended recognition tasks.
Vision-Language Models
Models like BLIP and PaliGemma understand both images and text, enabling:
Audio Processing
Hugging Face supports speech recognition, text-to-speech, speaker verification, and audio classification using models like Whisper and MMS.
The Spaces platform is particularly effective for deploying large language models:
Chatbots and Conversational AI
Find and locate objects in images with DETR (Detection Transformer) or YOLO networks and allow security systems, inventory systems and autonomous driving applications.
Code Generation
Models like CodeLLaMA can generate, debug, and explain code across multiple programming languages.
Content Generation
Create marketing copy, product descriptions, blog posts, or creative writing with fine-tuned language models.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
Combine language models with document retrieval to build systems that answer questions based on custom knowledge bases.
First, sign up for a free account at huggingface.co. Then, generate an API token:
# Clone your space repository
git clone https://huggingface.co/spaces/username/your-space-name
cd your-space-name
# Create a Python virtual environment
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate # On Windows: venv\Scripts\activate
# Install required packages
pip install gradio transformers torchCreate an app.py file with your Gradio or Streamlit application:
import gradio as gr
from transformers import pipeline
# Load sentiment analysis model
classifier = pipeline("sentiment-analysis")
def analyze_sentiment(text):
result = classifier(text)
return f"{result['label']}: {result['score']:.2%}"
# Create Gradio interface
demo = gr.Interface(
fn=analyze_sentiment,
inputs=gr.Textbox(placeholder="Enter text to analyze..."),
outputs="text",
title="Sentiment Analysis",
description="Analyze the sentiment of your text"
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
demo.launch()Create requirements.txt with your dependencies:
gradio==4.26.0
transformers==4.36.0
torch==2.1.0# Stage your changes
git add app.py requirements.txt
# Commit
git commit -m "Add sentiment analysis application"
# Push to Hugging Face Spaces
git pushYour application will automatically build and deploy. You can monitor the build process through the Spaces UI.
Beyond Spaces, the Hugging Face Inference API allows you to call models programmatically without hosting your own application. This is useful for integrating Hugging Face models into existing applications.
from huggingface_hub import InferenceApi
import requests
# Initialize the API
api = InferenceApi(repo_id="distilbert-base-uncased", token="YOUR_TOKEN")
# Text classification
result = api(inputs="I love this product!")
# Or use direct HTTP requests
headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer YOUR_TOKEN"}
response = requests.post(
"https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/distilbert-base-uncased",
headers=headers,
json={"inputs": "I love this product!"}
)
print(response.json())The Inference API is serverless, meaning you only pay for what you use. It scales automatically and integrates seamlessly with your applications, ideal for production deployments with variable traffic.
Select the correct Model Size. Smaller models such as DistilBERT or Llama2-7B have lower resource requirements and are faster compared with full-size models, and can exhibit little accuracy loss.
Use Mixed Precision: Enabling half-precision (fp16) during inference helps consume less memory and achieve more throughput.
Quantization: Convert models to int8 or int4 for even greater efficiency without significant accuracy degradation.
Batch Processing: Process multiple inputs simultaneously to maximize GPU utilization.
Caching: Cache model outputs for frequently requested inputs to reduce computational overhead.
Model Warm-Up: Pre-load models into memory during application startup to avoid cold-start latency.
API Authentication: Always use authentication tokens and never expose them in client-side code.
Rate Limiting: Implement rate limiting on your Spaces applications to prevent abuse.
Input Validation: Sanitize and validate user inputs to prevent injection attacks and ensure model robustness.
Monitoring and Logging: Track application performance, errors, and usage patterns for debugging and optimization.
| Feature | Hugging Face Spaces | Streamlit Cloud | Gradio.app | AWS Lambda |
| Ease of Use | Very Easy | Very Easy | Very Easy | Complex |
| AI-Focused | Yes | General Purpose | AI-Focused | General Purpose |
| Free Tier | Yes (CPU) | Yes | Yes | Limited |
| GPU Support | Paid | Paid | Paid | Available |
| Community | Massive AI Community | General Dev | AI Community | Enterprise |
| Infrastructure Management | None | None | None | Required |
| Model Integration | Native | Manual | Native | Manual |
While Hugging Face Spaces are free to create, you can monetize your AI applications in several ways:
Premium Models on Hugging Face Hub: Publish specialized models and charge for access or commercial licensing.
API Integration Services: Create Spaces that integrate Hugging Face models with custom business logic, then offer them as a service.
Model Fine-Tuning Services: Offer to fine-tune Hugging Face models for specific domains or use cases.
Custom Space Development: Build specialized Spaces for clients seeking AI solutions without the development effort.
Pro Subscription Features: Add paid tiers to your Spaces with enhanced capabilities, priority processing, or API access.
Cold Start Latency: Models need to be loaded before serving predictions. Solution: Use smaller models, quantization, or implement caching.
Rate Limiting: Free Spaces have request throttling. Solution: Upgrade to a paid GPU or implement client-side caching.
Model Size Limitations: Large models may exceed Space memory limits. Solution: Use quantization, model distillation, or API-based solutions.
Dependency Management: Complex dependency chains can cause build failures. Solution: Use Docker-based Spaces for full environment control.
Hugging Face and Spaces represent a paradigm shift in how machine learning models are developed, shared, and deployed. By removing infrastructure complexity and providing access to thousands of state-of-the-art models, they enable developers at all levels to build sophisticated AI applications.
Hugging Face has the infrastructure, tools and community support to make any of your AI and ML projects successful, whether your project is a basic sentiment analysis application, an NLP chatbot or a commercial computer vision system.The Transformers library, Model Hub and Spaces are parts of a holistic ecosystem that democratizes artificial intelligence.

Hassan Tahir wrote this article, drawing on his experience to clarify WordPress concepts and enhance developer understanding. Through his work, he aims to help both beginners and professionals refine their skills and tackle WordPress projects with greater confidence.